This is part 2 of How to deploy your Django app on Linode. You can read Part 1 here
Configure settings.py like so

proj/settings.py
Step 1. Add the following lines in your proj/settings.py
BASE_URL = 'https://YOU_DOMAIN.com'
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['buildwebsite.io', 'localhost']
CSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINS = ['https://buildwebsite.io', 'http://localhost:8000']
Debug = False # Make sure to change this to FalseStep 2. Upload your code onto a Github repo
Step 3. Run the following command from your Linode
cd /var/www/django_app/
git clone YOUR_REPO
Step 4. My app is called “django-demo”, and I have cloned it into my Linode. Install any necessary packages or dependencies. Be sure to run it in virtual env
This is what I have after cloning the repo
# Activate the virtual env
source /var/www/django_app/djangoenv/bin/activate
cd /var/www/django_app/YOUR_DJANGO_APP/
pip install -r requirements.txt
python manage.py migrateInstall Node if necessary (side quest)
My app uses the django-tailwind package and it requires Node to be installed. Since this is a fresh VPS, I will need to install Node
This is the error message I got

Error message

Successfully installed Node
Just before we go any further, I’d do a quick check to see everything is working fine by running
python manage.py runserver IP:PORT
Django is running fine
Back to the main quest
Set up Gunicorn and Nginx
Step 5. Run the following command to install gunicorn
pip install gunicornStep 6. Check that Nginx is installed (it should)
nginx -vIf you get the version number, then Nginx is there. If not, running the following commands
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx
sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginxStep 7. You need a gunicorn service file for each app at /etc/systemd/system/YOUR_APP_NAME.service
In my case, my app is called “django-demo”, I’d create /etc/systemd/system/django_demo.service file
Notice I am not using hyphen (-) in the nomenclature. Run the following command
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/django_demo.serviceInclude the following in the file
[Unit]
Description=Gunicorn instance to serve django_demo
After=network.target
[Service]
User=root
Group=www-data
WorkingDirectory=/var/www/django_app/django-demo
ExecStart=/var/www/django_app/djangoenv/bin/gunicorn --access-logfile - --workers 3 --bind unix:/var/www/django_app/django_demo.sock proj.wsgi:application
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetReplace “django-demo”, “django_demo” with your app name
Step 8. Each application needs its own Nginx conf
Run:
sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/django-demoAnd add the following to the file:
server {
listen 80;
server_name buildwebsite.io;
location / {
include proxy_params;
proxy_pass http://unix:/var/www/django_app/django_app.sock;
}
}Step 9: Create a master Nginx config file at /etc/nginx/conf.d/nginx.conf and add the following
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;Step 10: Enable and start gunicorn service
sudo systemctl start django_demo.service
sudo systemctl enable django_demo.serviceYou can run this line to make sure gunicorn service is up and running
sudo systemctl status django_demo.serviceIf it’s running fine, you should be able to see this
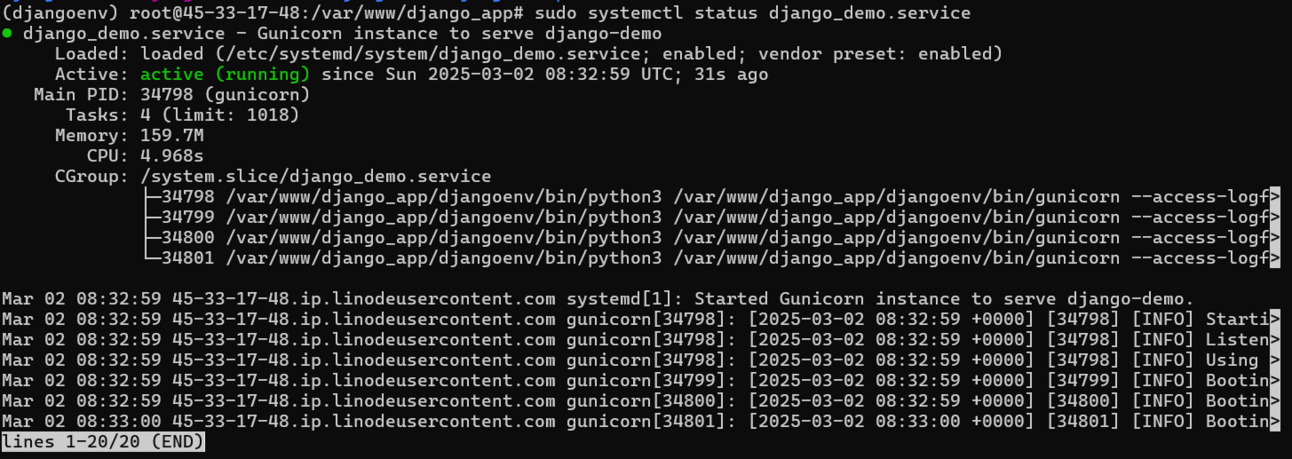
Gunicorn running fine
Step 11. Enable, test and restart Nginx service by running the following commands
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/django-demo /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginxYou should be able to get
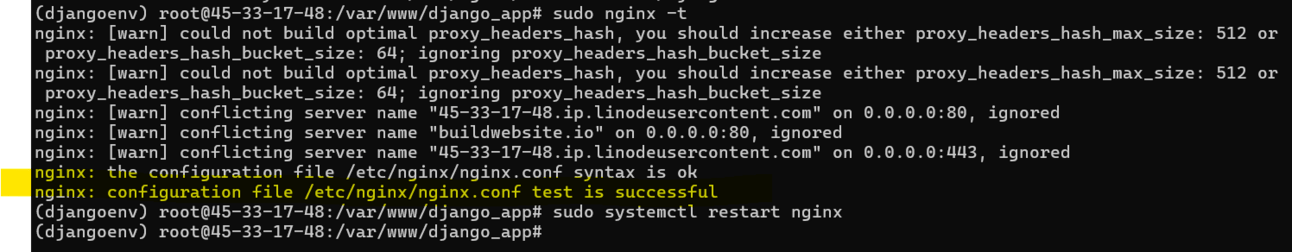
Nginx test is successful
Set up SSL for the domain
Step 12. Install certbot
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ufw
sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw allow http
sudo ufw allow https
sudo ufw enable
# Install snapd
sudo apt-get install snapd
sudo snap install core
sudo snap refresh core
# Install certbot
sudo apt-get remove certbot
sudo snap install --classic certbot
sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbotStep 13. Request an SSL certificate
sudo certbot --nginx -d buildwebsite.ioIf that’s successful, you should be able to see:
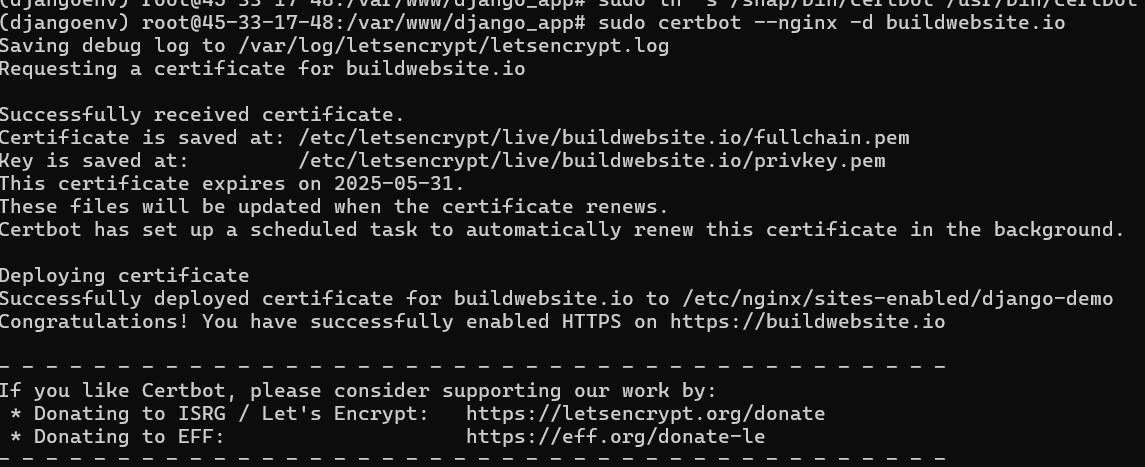
Successfully installed SSL certificate
Step 14. And viola! It’s done. If you type your domain name into the browser, you should be able to see it!

My Django app has been deployed!
That’s it!
Hi, my name is George. My goal is to build apps, make money and quit my job. If you like to learn about copywriting, marketing and technical how-to’s like this blog post, be sure to subscribe to my newsletter!